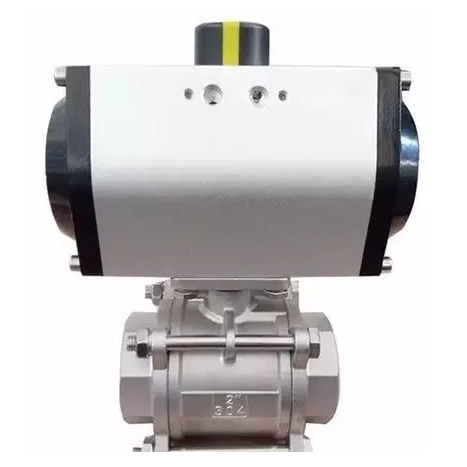
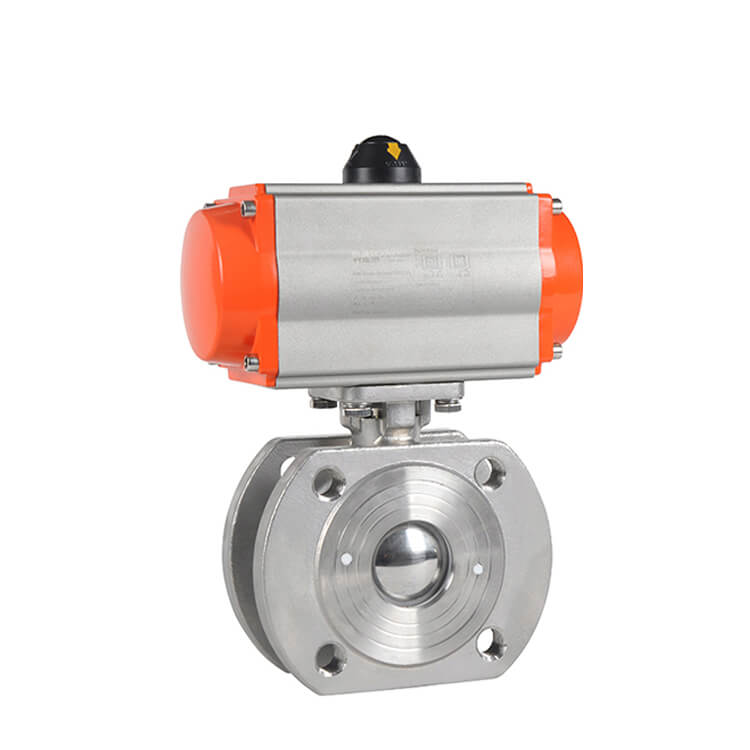
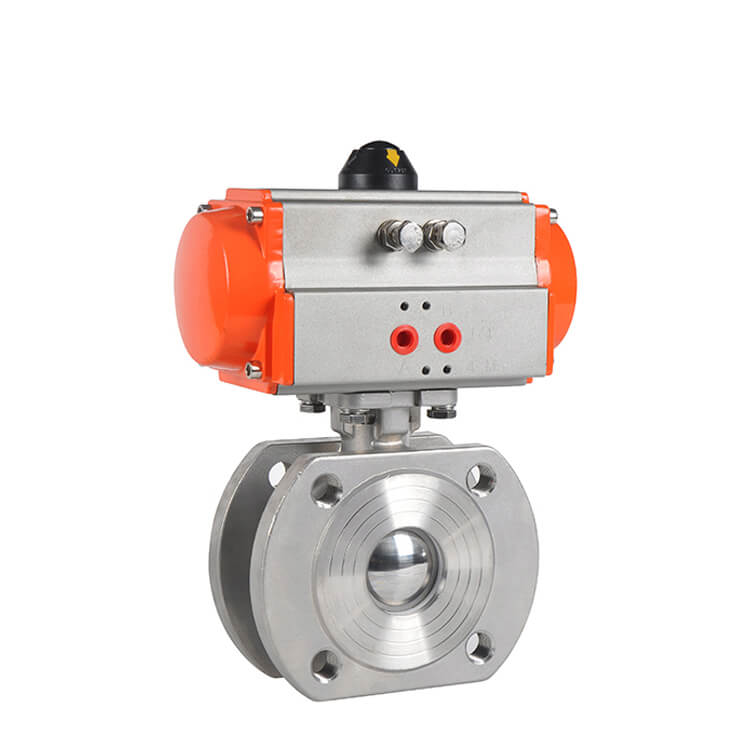
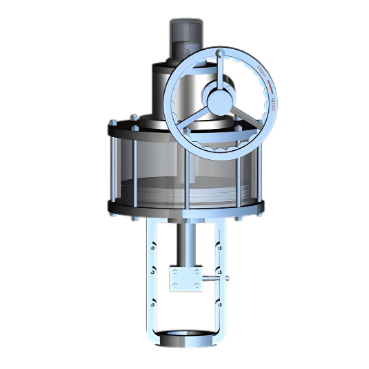
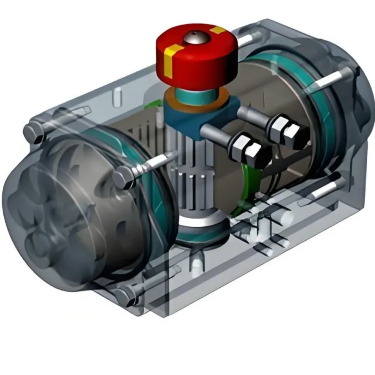
A valve pneumatic actuator operates based
on the power of compressed air to control the movement of valves. It mainly
consists of a housing, a piston or diaphragm, and a connecting rod.
When the system is activated, compressed
air from a reliable source, such as an air compressor, enters the actuator. In
piston - type actuators, the air pressure acts on the piston. As the air fills
one side of the piston chamber, it generates a force that pushes the piston to
move linearly. This movement is then transferred through the connecting rod to
the valve stem. The valve stem, in turn, opens, closes, or modulates the valve,
regulating the flow of fluids like gases or liquids within a pipeline.
For diaphragm - type actuators, the
principle is similar. Compressed air presses against the flexible diaphragm.
The diaphragm, being made of a resilient material, deforms under the air
pressure. This deformation causes the attached connecting rod to move, which
controls the valve's operation. The beauty of pneumatic actuators lies in their
simplicity and quick response time. They can be easily controlled by adjusting
the air pressure, enabling precise and efficient valve operation in various
industrial applications, including chemical plants, oil refineries, and water
treatment facilities.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com