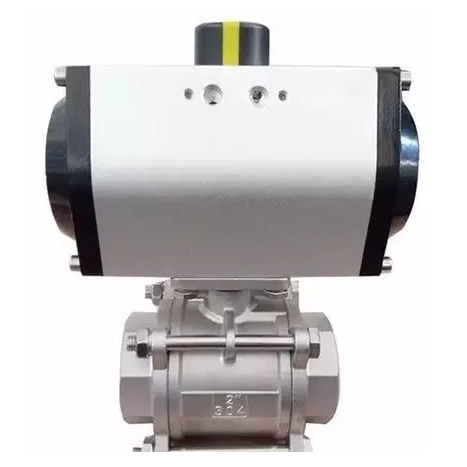
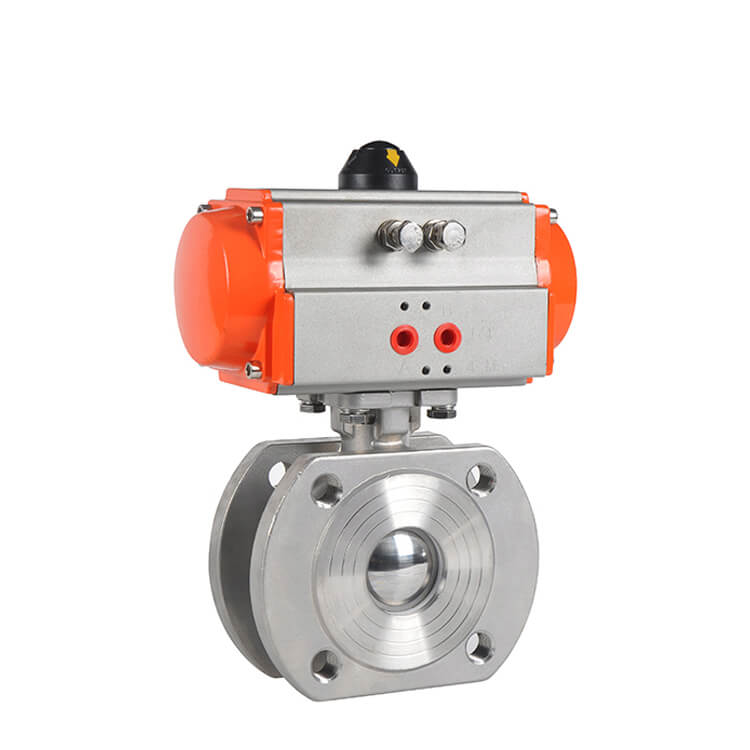
Single - acting and double - acting
pneumatic actuators are two common types of actuators used in various
industrial applications. Here's a comparison between them:
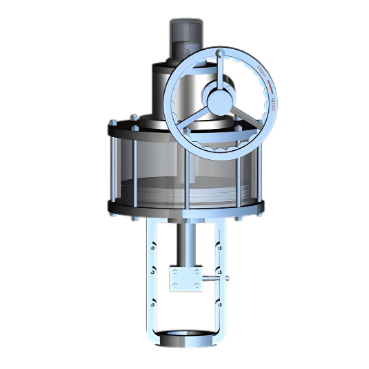
Operating Principle: Single - acting
pneumatic actuators use compressed air to move in one direction and rely on a
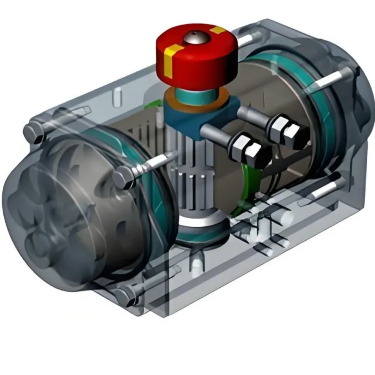
spring or other external force to return to their original position. Double -
acting pneumatic actuators, on the other hand, use compressed air to move in
both directions, providing more precise control and faster response times.
Force and Torque: Double - acting actuators
generally produce higher force and torque compared to single - acting
actuators. This is because they can utilize the full power of the compressed
air in both directions of operation. Single - acting actuators, with their
spring - return mechanism, may have limitations in the force they can exert,
especially during the return stroke.
Applications: Single - acting actuators are
often used in applications where a simple, one - way motion is required, such
as in valves that need to be opened or closed in a specific position and do not
require rapid or precise control. Double - acting actuators are preferred in
applications that demand high - speed operation, precise positioning, and
greater force, such as in industrial automation, robotics, and some types of
process control systems.
Cost and Complexity: Single - acting
actuators are usually less expensive and have a simpler design compared to
double - acting actuators. They require fewer components and a less complex air
- supply system. Double - acting actuators, with their more elaborate design
and need for a dual - air supply, tend to be more costly and complex to install
and maintain.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com