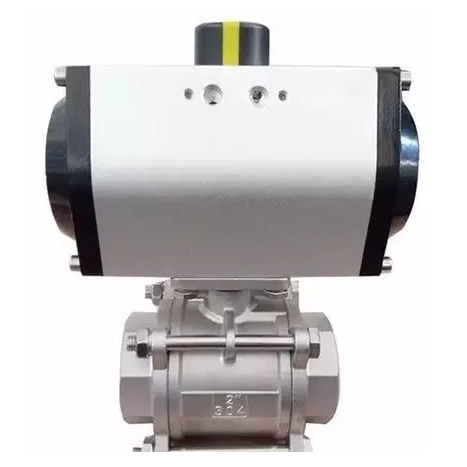
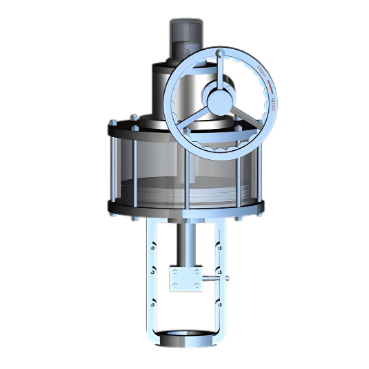
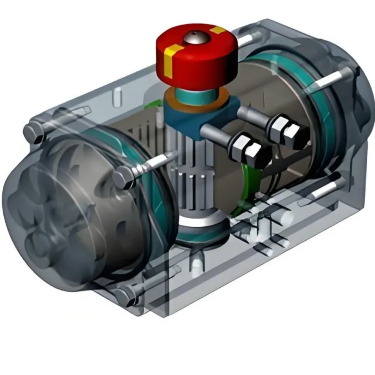
A rotary pneumatic actuator is a device that drives mechanical components to rotate through compressed air, and is widely used in industrial automation, valve control, robotics, and other fields. Its core advantages lie in high torque output, fast response, and adaptability to harsh environments.
2、 Working principle
Power source: Compressed air (usually pressure range 0.4-1.0 MPa) is input into the actuator through the air supply pipeline.
Motion conversion:
Blade type: The internal blades are rotated by air pressure, resulting in angular displacement (commonly 90 ° or 180 °).
Gear and rack type: Pneumatic driven piston converts linear motion into rotational motion through a gear and rack structure.
Control method: By adjusting the airflow direction and flow rate through solenoid valves, precise angle control can be achieved.
3、 Main types and characteristics
Type advantages and disadvantages
Compact blade structure, fast response, and low torque
Gear rack high torque, strong durability, large volume, high cost
4、 Core application areas
Industrial valve control: opening and closing of ball valves and butterfly valves in petrochemical pipelines.
Automated production line: The gripping and rotating actions of the end effector of a robotic arm (such as an automotive assembly line).
Food and Medicine: Oil free lubricated actuators that meet hygiene standards are used in filling equipment.
In the field of new energy: In the emerging trend of 2025, the demand for sealing control of hydrogen energy pipelines is expected to increase significantly.
5、 Technical advantages and limitations
Advantages:
✅ Explosion resistant and explosion-proof, suitable for flammable and explosive environments (such as natural gas pipelines).
✅ Low maintenance cost, with a lifespan of over 100000 cycles.
Limitations:
❌ Relying on a stable gas source, humidity and impurities may affect performance.
❌ The control accuracy (± 1 °) is slightly lower than that of electric actuators.
6、 Technological Innovation in 2025
Intelligent upgrade: Integrated IoT sensors, real-time monitoring of torque and angle, and feedback to the cloud (such as Siemens SIPART series).
Energy saving design: Adopting a dual pressure chamber structure, the utilization rate of compressed air is increased by 30%.
Material innovation: Carbon fiber composite materials reduce weight while maintaining corrosion resistance.
7、 Selection and maintenance suggestions
Selection parameters: torque requirement (Nm), rotation angle, interface size (ISO 5211 standard).
Maintenance points:
Regularly clean the air source filter to prevent particle blockage.
Check the wear of seals every quarter to avoid air leakage.
8、 Conclusion
Rotary pneumatic actuators remain the core driving solution in the field of industrial automation due to their reliability and economy. With the breakthroughs in intelligence and new material technology, its application in the fields of new energy and high-end manufacturing will further expand.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com