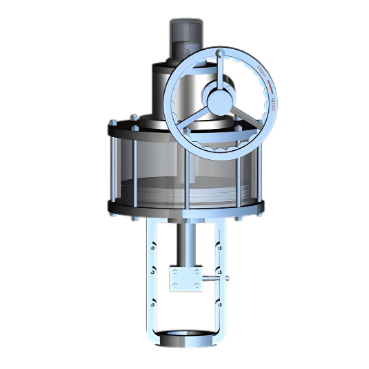
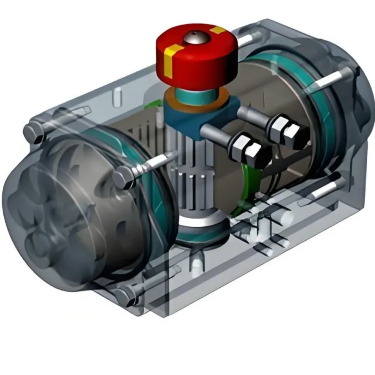
Durability testing of compact pneumatic
actuators is essential to ensure they can withstand long - term use under
various conditions. The following procedures are commonly adopted.
First, cyclic testing is a fundamental
approach. The actuator is repeatedly cycled between its extended and retracted
positions for a predefined number of times, often in the thousands or even millions.
During this process, parameters such as force output, stroke length, and
response time are continuously monitored. Any significant degradation in these
aspects may indicate potential wear or failure of internal components like
pistons, seals, or cylinders.
Second, environmental testing exposes the
actuator to extreme conditions. This includes subjecting it to high and low
temperatures, humidity, and corrosive atmospheres. For example, in high -
temperature tests, the actuator is placed in an oven - like chamber and
operated at elevated temperatures to assess how heat affects its performance
and material integrity. In humidity tests, the actuator is kept in a chamber
with controlled moisture levels to check for any adverse effects on seals and
metal parts, such as rusting or swelling of elastomeric components.
Finally, load - endurance testing involves
applying a constant or varying load to the actuator while it operates. This
simulates real - world working conditions where the actuator has to overcome resistance.
By observing how the actuator performs under load over an extended period,
engineers can determine its ability to maintain functionality and durability,
helping to identify potential weak points and improve the overall design.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com