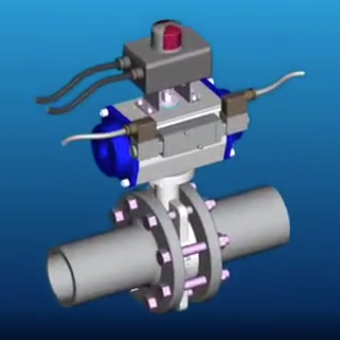
Introduction
Pneumatic rotary actuator cylinders combine linear and rotational motion capabilities in a single compact unit, making them essential components in modern automation systems. These devices convert compressed air energy into controlled rotary movement through innovative mechanical designs.
Working Principle
The pneumatic rotary actuator cylinder operates through two primary mechanisms:
- Rack-and-pinion system: Compressed air drives a piston connected to a rack gear, which engages with a pinion gear to produce rotation
- Scotch yoke mechanism: Linear piston motion gets converted to rotary output via a sliding yoke and crank arrangement
Key performance characteristics include:
- Typical rotation angles: 90°, 180°, or 270°
- Operating pressures: 4-7 bar (60-100 psi)
- Torque outputs ranging from 1 Nm to 500 Nm
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Recent research demonstrates that optimizing gas supply pressure through power-matching methods can significantly improve energy efficiency in pneumatic rotary actuator systems1. Experimental verification shows:
- 15-20% energy savings possible through pressure optimization
- Reduced air consumption without compromising performance
Comparative Analysis
When compared to electric actuators, pneumatic rotary actuator cylinders offer:
- Faster response times
- Higher power-to-weight ratios
- Better suitability for hazardous environments
- Lower maintenance requirements
However, electric actuators provide more precise positioning capabilities in certain applications.
Industrial Applications
These versatile components find use across multiple industries:
-
Valve automation:
- Quarter-turn ball valves
- Butterfly valves
- Plug valves
-
Material handling:
- Indexing tables
- Part positioning systems
- Conveyor diverters
-
Packaging machinery:
- Rotary sealing heads
- Capping stations
- Label applicators
Selection Criteria
Key parameters for proper actuator selection include:
Maintenance Best Practices
To ensure optimal performance and longevity:
- Regularly inspect seals and bearings
- Maintain proper air filtration (40 micron or better)
- Monitor lubrication requirements
- Periodically verify torque output
Future Developments
Emerging trends in pneumatic rotary actuator technology include:
- Integrated position feedback systems
- Smart sensors for predictive maintenance
- Hybrid electro-pneumatic designs
- Lightweight composite materials
These advancements aim to bridge the performance gap between pneumatic and electric actuation systems while maintaining pneumatic advantages.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com