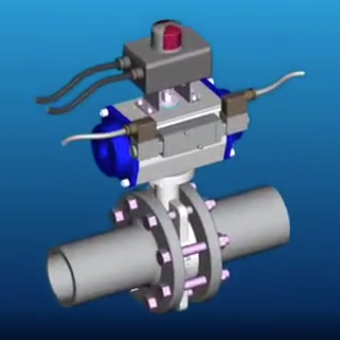
Pneumatic air actuators are essential components in modern industrial automation, offering reliable and efficient motion control through compressed air. These devices convert energy from pressurized air into mechanical motion, making them ideal for applications requiring quick, precise, and repeatable movements.
How Pneumatic Air Actuators Work
Pneumatic actuators operate by using compressed air to generate linear or rotary motion. The most common types include:

- Single-acting actuators – Use air pressure to move in one direction, with a spring returning them to the original position.
-

- Double-acting actuators – Utilize air pressure for both extending and retracting movements, providing better control and force output.
Key Advantages
- High Speed & Responsiveness – Compressed air allows for rapid actuation, making them suitable for high-cycle operations.
- Durability & Low Maintenance – With fewer moving parts than hydraulic or electric actuators, they require minimal upkeep.
- Safety in Hazardous Environments – Since they don’t generate sparks, they are safe for explosive or flammable settings.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Air is readily available, reducing operational costs compared to hydraulic or electric alternatives.
Common Applications
- Manufacturing & Assembly Lines – Used in clamping, pressing, and material handling.
- Packaging Machinery – Ensure precise product positioning and sealing.
- Automotive Industry – Control robotic arms and assembly processes.
- Food & Beverage Processing – Preferred for hygienic, corrosion-resistant operations.
Choosing the Right Actuator
When selecting a pneumatic actuator, consider:
- Force & Stroke Requirements – Ensure the actuator can handle the load and travel distance.
- Operating Pressure – Match the actuator’s pressure range with the available air supply.
- Environmental Conditions – Select materials (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) that resist corrosion or extreme temperatures.
Future Trends
With advancements in smart pneumatics, IoT-enabled actuators are emerging, allowing remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Energy-efficient designs are also gaining traction to reduce compressed air consumption.
Conclusion
Pneumatic air actuators remain a cornerstone of industrial automation due to their speed, reliability, and cost efficiency. Whether in heavy-duty manufacturing or delicate assembly tasks, they continue to drive productivity across industries.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com