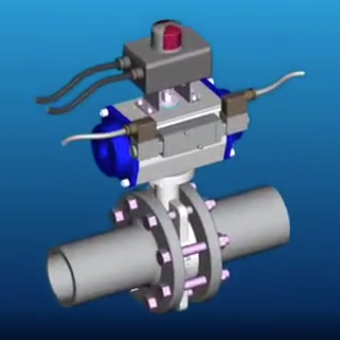
Introduction
Pneumatic actuators are widely used in industrial automation, process control, and robotics due to their reliability, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. These devices convert compressed air energy into mechanical motion, providing linear or rotary movement for valves, grippers, and other automation components. This article explores the essential features of pneumatic actuators and their advantages in various applications.
Key Features of Pneumatic Actuators
1. High Speed and Responsiveness
- Pneumatic actuators operate at high speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid motion, such as pick-and-place robots and assembly lines.
- They provide instantaneous response to control signals, ensuring quick actuation when needed.
2. Simple and Robust Design
- Unlike electric or hydraulic actuators, pneumatic actuators have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance requirements.
- Their durable construction (often made of aluminum, stainless steel, or reinforced plastics) ensures long service life even in harsh environments.
3. High Force-to-Weight Ratio
- Despite their compact size, pneumatic actuators can generate high force output, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- They are lightweight, which is beneficial in robotics and aerospace applications.
4. Safety and Explosion-Proof Operation
- Since they use compressed air instead of electricity, pneumatic actuators are inherently safe in explosive or flammable environments (ATEX-certified models available).
- No risk of sparks, overheating, or short circuits.
5. Adjustable Stroke and Positioning
- Many pneumatic actuators allow adjustable stroke lengths, enabling precise control over movement range.
- Some models feature cushioning mechanisms to reduce impact at the end of the stroke, improving precision and reducing wear.
6. Fail-Safe Operation
- Pneumatic actuators can be designed with spring-return mechanisms, ensuring they return to a safe position in case of air supply failure.
- This feature is critical in safety-critical applications like emergency shut-off valves.
7. Energy Efficiency and Low Operating Costs
- Compressed air is an energy-efficient power source compared to hydraulic or electric systems.
- Minimal energy loss, as air can be exhausted directly without requiring recirculation.
8. Versatility in Motion Types
- Linear actuators (single or double-acting) for push-pull motions.
- Rotary actuators (rack-and-pinion, vane, or helical designs) for angular movement.
- Rodless actuators for applications requiring long strokes in compact spaces.
9. Easy Integration with Control Systems
- Compatible with solenoid valves, position sensors, and PLCs for automated control.
- Some advanced models include smart positioners for real-time feedback and adjustments.
10. Low Maintenance Requirements
- No lubrication needed in many cases (self-lubricating seals available).
- Resistant to dust, moisture, and corrosion when properly sealed.
Applications of Pneumatic Actuators
Due to their features, pneumatic actuators are used in:
✅ Industrial Automation (assembly lines, packaging machines)
✅ Process Control (valve actuation in oil & gas, water treatment)
✅ Robotics (grippers, robotic arms)
✅ Food & Beverage (sanitary-grade actuators)
✅ Automotive (brake systems, clamping devices)
Conclusion
Pneumatic actuators offer speed, reliability, safety, and cost-efficiency, making them a preferred choice in many industries. Their adjustability, fail-safe operation, and low maintenance further enhance their appeal. When selecting a pneumatic actuator, consider factors such as force requirements, environmental conditions, and control integration to ensure optimal performance.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com