Introduction
In the realm of industrial automation, heavy-duty pneumatic rotary actuators stand as critical components for converting compressed air energy into controlled rotational motion. Designed to withstand harsh environments, high torque demands, and continuous operation, these actuators are indispensable in industries ranging from manufacturing and oil and gas to mining and renewable energy. This article explores the design principles, applications, advantages, and future trends of heavy-duty pneumatic rotary actuators.
Design and Working Principles
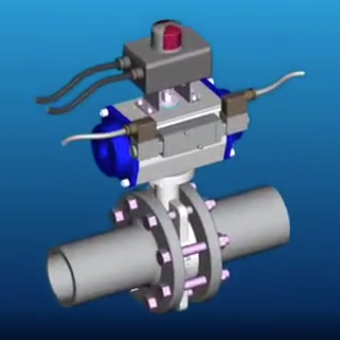
A pneumatic rotary actuator operates by harnessing compressed air to generate rotational force. Heavy-duty variants are engineered with robust materials such as anodized aluminum, stainless steel, or reinforced polymers to endure extreme pressures (typically 6–12 bar), corrosive conditions, and mechanical stress.
Key Components:
-
Piston or Vane Mechanism:
- Rack-and-pinion or vane-type designs translate linear air pressure into rotary motion. Heavy-duty models often use dual-piston configurations for balanced torque output.
-
Seals and Bearings:
- High-grade nitrile or fluorocarbon seals ensure leak-proof performance, while hardened bearings reduce friction and wear.
-
Rotation Angle:
- Adjustable rotation angles (90°, 180°, or multi-turn) allow customization for valve control, material handling, or robotic arms.
-
Mounting Options:
- Flange, foot, or clevis mounts enable integration with valves, conveyors, and other machinery.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Heavy-duty pneumatic rotary actuators excel in scenarios demanding high torque, rapid response times, and explosion-proof operation. Notable use cases include:
1. Valve Automation in Process Industries
- Used to control ball valves, butterfly valves, or dampers in chemical plants, water treatment facilities, and oil refineries. Their fail-safe designs ensure shutdowns during power outages.
2. Material Handling Systems
- Drive conveyor belt diverters, palletizers, and sorting arms in logistics centers. Pneumatic actuators offer faster cycle times compared to electric alternatives.
3. Mining and Heavy Machinery
- Operate drilling equipment, crushers, and excavators where dust, moisture, and vibration are prevalent.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
- Adjust solar panel angles or wind turbine blade pitch for optimal energy capture.
Advantages Over Competing Technologies
While electric and hydraulic actuators have their niches, heavy-duty pneumatic actuators dominate in specific areas:
-
High Power-to-Weight Ratio:
- Deliver exceptional torque (up to 50,000 Nm in some models) without the bulk of hydraulic systems.
-
Intrinsic Safety:
- No risk of sparks, making them ideal for explosive atmospheres (ATEX/IECEx certified).
-
Low Maintenance:
- Fewer moving parts and no need for lubrication reduce downtime.
-
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Lower initial costs and energy consumption compared to electric servo motors.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Despite their strengths, heavy-duty pneumatic actuators face limitations:
- Air Supply Dependency: Requires clean, dry compressed air; moisture filters and regulators are essential.
- Limited Positioning Accuracy: Not ideal for precision tasks; hybrid electro-pneumatic systems may bridge this gap.
- Noise Levels: Silencers and mufflers can mitigate operational noise.
Future Trends and Innovations
The evolution of heavy-duty pneumatic actuators aligns with Industry 4.0 demands:
-
Smart Actuators:
- Integration with IoT sensors for predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring.
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Advanced air-recycling systems to minimize compressed air waste.
-
Lightweight Composite Materials:
- Carbon fiber-reinforced components for higher strength-to-weight ratios.
Conclusion
Heavy-duty pneumatic rotary actuators remain a cornerstone of industrial automation, offering unmatched durability, safety, and cost efficiency. As industries push toward smarter and greener solutions, continuous innovation in actuator design will ensure their relevance in tomorrow’s automated world. Engineers and system designers must evaluate operational requirements carefully to leverage the full potential of these powerful devices.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com