Introduction
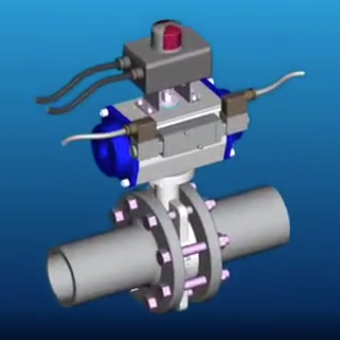
Electro-pneumatic actuators are hybrid devices that combine electrical control with pneumatic actuation to achieve precise and efficient motion control. These actuators are widely used in industrial automation, process control, and robotics due to their reliability, fast response, and adaptability to various operating conditions.
Electro-Pneumatic Actuators Working Principle
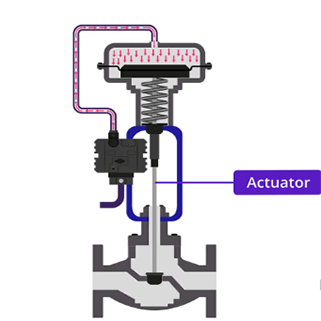
An electro-pneumatic actuator consists of three main components:
- Electrical Control Unit – Typically a solenoid valve or a digital positioner that receives electrical signals (e.g., 4-20 mA, 0-10 V, or digital commands) to regulate airflow.
- Pneumatic Actuator – Converts compressed air into mechanical motion, either linear (piston-type) or rotary (rack-and-pinion or vane-type).
- Feedback Mechanism – Many modern electro-pneumatic actuators incorporate position sensors (e.g., potentiometers or encoders) for closed-loop control, ensuring high precision.
When an electrical signal is sent to the control unit, it modulates the air supply to the pneumatic actuator, causing movement. The feedback system ensures the actuator reaches the desired position accurately.
Key Applications
Electro-pneumatic actuators are used in industries requiring precise and rapid motion control, including:
- Process Industries – Valve control in oil & gas, chemical, and water treatment plants.
- Manufacturing – Automation of assembly lines, material handling, and packaging.
- Robotics – Gripping and positioning mechanisms in robotic arms.
- Automotive – Brake and clutch systems, as well as test rigs.
Electro-Pneumatic Actuators Advantages Over Other Actuators
Compared to purely pneumatic or electric actuators, electro-pneumatic actuators offer:
- High Speed & Force – Pneumatic systems provide rapid movement, while electrical control ensures precision.
- Energy Efficiency – Consumes less power than fully electric actuators for high-force applications.
- Reliability & Durability – Fewer moving parts than electric motors, reducing wear and maintenance.
- Safety – No risk of overheating or sparking in explosive environments (when properly designed).
Conclusion
Electro-pneumatic actuators bridge the gap between pneumatic power and electronic precision, making them indispensable in modern automation. Their versatility, efficiency, and robustness ensure continued adoption across multiple industries. Future advancements may include smarter IoT integration and improved energy-saving designs.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com