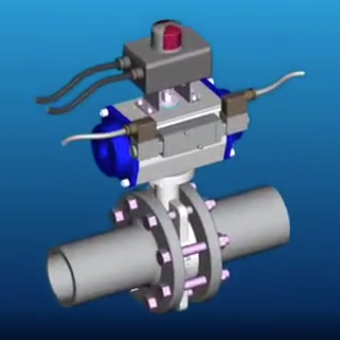
Introduction
Pneumatic rotary actuators are critical components in industrial automation, offering precise angular motion control through compressed air. Among these, 90-degree rotation pneumatic rotary actuators stand out for their ability to deliver rapid, reliable, and cost-effective quarter-turn operations. This article explores the design principles, key applications, and advantages of these actuators, emphasizing their role in modern manufacturing and process control systems.

1. Working Principle and Design
A 90-degree pneumatic rotary actuator converts linear pneumatic energy into rotational motion, typically achieving a precise quarter-turn (90°) output. The mechanism relies on compressed air acting on pistons, vanes, or gears within the actuator:
- Vane-Type Design: A single vane mounted on a central shaft rotates within a cylindrical chamber. Differential air pressure on either side of the vane generates torque, enabling swift 90° rotation.
- Rack-and-Pinion Design: Dual pistons drive a linear rack, which meshes with a central pinion gear to produce rotary motion. This design excels in high-torque applications.
Key components include corrosion-resistant aluminum or stainless-steel housing, high-durability seals (e.g., Nitrile or PTFE), and precision bearings to minimize friction. The compact, modular design allows easy integration with valves, grippers, or indexing tables.
2. Performance Characteristics
- Torque Output: Ranges from 1 Nm to over 1,000 Nm, depending on bore size and air pressure (typically 4–8 bar).
- Speed: Adjustable via flow control valves, achieving rotation times as low as 0.1 seconds.
- Accuracy: Repeatability within ±0.5° ensures consistent positioning, critical for automated processes.
- Environmental Resilience: Resistant to extreme temperatures, dust, and moisture. Explosion-proof variants comply with ATEX/IECEx standards for hazardous areas.
3. Industrial Applications
- Valve Automation: Widely used in ball and butterfly valves for process industries (oil/gas, chemical, water treatment). Actuators provide fail-safe operation, closing/opening valves during emergencies.
- Material Handling: Rotating parts in conveyors, sorting systems, or palletizers.
- Assembly Lines: Positioning components in automotive or electronics manufacturing (e.g., screwdriving, part insertion).
- Food and Pharma: Hygienic models with FDA-compliant seals prevent contamination in packaging or filling machines.
4. Advantages Over Electric and Hydraulic Alternatives
- Simplicity and Cost: No complex electronics; reduced maintenance compared to electric actuators.
- Safety: No fire risk from sparks, ideal for flammable environments.
- High Power Density: Delivers greater torque per unit size than electric motors.
- Rapid Response: Faster cycle times due to air compressibility and lightweight components.
5. Selection Criteria
When specifying a 90-degree pneumatic rotary actuator, consider:
- Torque Requirements: Account for startup inertia and operational load.
- Rotation Angle: Ensure exact 90° output (adjustable end stops may be needed).
- Air Supply: Match port sizes and pressure ratings to existing systems.
- Environment: Select materials and seals compatible with temperature, chemicals, or washdown conditions.
- Accessories: Position sensors, manual overrides, or speed controllers enhance functionality.
6. Maintenance and Optimization
- Regularly inspect seals and lubricate moving parts to prevent leaks and wear.
- Use filtered, dry air to avoid internal corrosion.
- Monitor cycle counts and replace consumables (e.g., O-rings) per manufacturer guidelines.
7. Future Trends
Smart actuators with embedded IoT sensors are emerging, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time torque feedback. Additionally, energy-efficient designs reduce air consumption, aligning with sustainability goals.
Conclusion
The 90-degree pneumatic rotary actuator remains a cornerstone of industrial automation, balancing performance, durability, and cost. As industries prioritize efficiency and safety, advancements in materials and smart technology will further solidify its role in next-generation systems. Engineers must leverage its strengths while adhering to rigorous selection and maintenance protocols to maximize operational uptime.
If you want to learn more about low-priced products, please visit the following website: www.xm-valveactuator.com